Bushing Naming Conventions
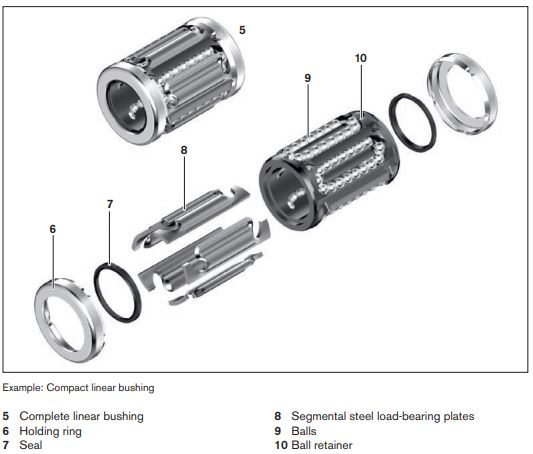
Ball Retainer- The rows of balls circulate in closed circuits in the ball retainer. Typically allows for the first row of balls to be in contact with the shaft, while the re-circulating balls are not subjected to loading.
Steel Sleeve/Steel Segmented Loading Plates– transmits the forces applied from outside to the balls.
Seals and Holding Rings- The seals protect the linear bushings from contamination and the holding rings keep the steel load-bearing plates in the desired position.
Precision Steel Shafts- Precision steel shafts are available as solid
and tubular shafts. There are shaft support blocks or shaft support rails for holding the shafts. Just like the linear sets, these standardized units can significantly reduce installation time. No expensive joining structure is required because the shaft is simply fastened by screwing down the block or rail.
Shaft Support Blocks- The precision steel shafts can be fastened using shaft support blocks, without the need for any further processing. The shaft is slid into the bore in the shaft support block and fixed with a set screw.
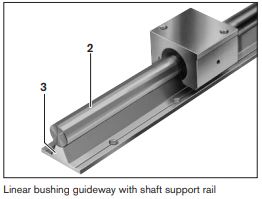
Shaft Support Rails- The use of shaft support rails prevents shaft deflection. To fasten the shaft to the shaft support rail, radial threaded holes must be made in the shaft along its entire length to accommodate the fixing screws for joining the two parts.
Ball Recirculation- The type of ball recirculation is an important distinguishing feature of linear bushings. This has a direct effect on the linear bushing’s load capacity and its overall dimensions.
Tangential Recirculation- In tangential recirculation, the balls are returned
to the load-bearing zone from the side. These linear bushings are distinguished by their small space requirement (small outside diameter). This
group comprises:
1. Compact and eLINE linear bushings
2. Super linear bushings
3. Standard linear bushings
4. Segmental linear bushings
5. Torque-resistant linear bushings
6. Linear bushings for combined linear and rotary motion
Radial Recirculation- In radial recirculation, the ball return channel is
located above the load-bearing zone. This construction principle permits a larger number of load-bearing rows of balls for the same shaft diameter and therefore higher load capacities. This group comprises of Radial linear bushings.
Next Page: Bushings Selection Guide
Previous Page: Bushings Theory