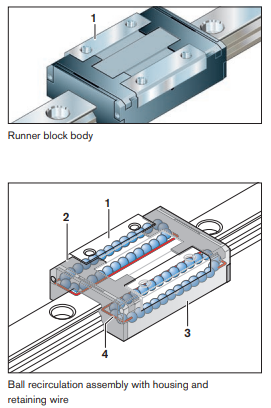
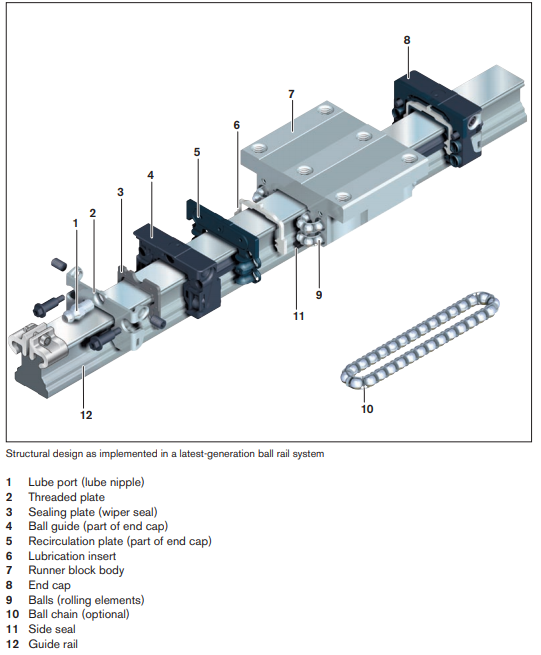
A ball rail system (BRS) consists of a guide rail and runner blocks. The BRS has 4 rows of balls in an O-arrangement with a contact angle of 45°. The balls are in 2-point contact with the rail and the runner block (see illustration). The guide rail has four running tracks along which one or more runner blocks can travel. The guide rail can be bolted into place from above or below. V-guide rails are pressed into the mounting base. Depending on the requirements, the runner block has either through-bores or threaded holes for direct mounting to the adjoining structure. Ball runner blocks are available in various sizes, designs and preload classes, thus covering a wide range of applications. The ball rail system is the most versatile of all the profiled rail systems. It is offered in many different versions (see section 3.2.3.1).
- High load capacities in all four major planes of load application
- High system rigidity
- Limitless interchangeability due to precision manufacturing
- Smooth running performance
- Zero-clearance movement
- Excellent high-speed characteristics
- Easy-to-achieve precision
- Very good travel accuracy with HP series runner blocks
- Long-term zero maintenance
- Minimum quantity lubrication system with integrated reservoir for oil lubrication (depending on version)
- Lube ports on all sides
- Optional ball chain
- Broad range of accessories for industry specific solutions (seals, wipers/scrapers)
- High dynamic characteristics with high-speed runner blocks
- Optimum installation error compensation with super runner block
- Integrated, inductive and wear-free measuring system as an option
- Runner blocks in rust- and acid-resistant steel to EN 10088 available
- Up to 60% weight saving with aluminum runner block
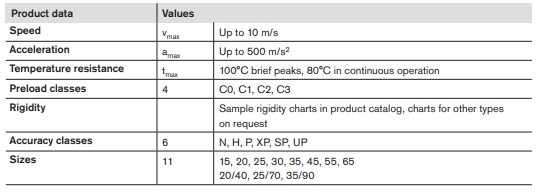
Structural Design
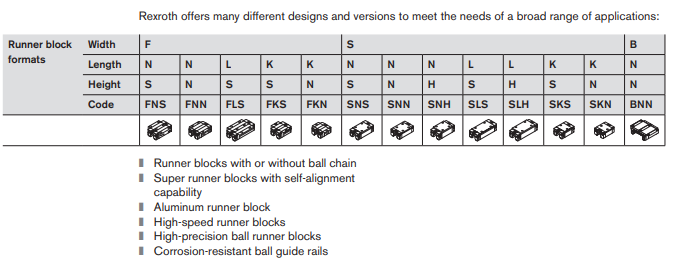
Versions
Application Areas